Terminators
When you have an Adze log instance, and have applied your desired modifiers, you must terminate the method chain. The methods used to terminate the chain are called terminators.
Adze comes with 9 default log level terminators, all of which can be configured.
| Level | Name | Standard Method Used |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | alert | error |
| 1 | error | error |
| 2 | warn | warn |
| 3 | info | info |
| 4 | fail | info |
| 5 | success | info |
| 6 | log | log |
| 7 | debug | debug |
| 8 | verbose | debug |
In addition to the default log levels, Adze provides a handful of other special terminators.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| clear / clr | An alias for console.clear(). |
| custom | Allows you to generate a log for a custom log level. |
| seal | Allows you to create a child logger by sealing your log chain into a new logger class. |
| sealTag | Allows you to create a child logger by sealing your log chain into a template string literal tag function. |
| thread | Creates a context thread that can capture data points throughout multiple scopes of your application. |
Level Terminators
These are the basic level terminators that come with Adze by default.
alert
This level should only be used for logs that require immediate attention. This should be used sparingly and only for the most critical of errors.
Default log level = 0
Standard Log Method: console.error()
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class BaseLog {
public alert(...args: unknown[]): void;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
adze.alert('Something went horribly wrong!');
// With emoji's enabled
adze.withEmoji.alert('Something went horribly wrong!');
Browser Output

Server Output

error
Use this for logging fatal errors or errors that impact functionality of your application.
Default log level = 1
Standard Log Method: console.error()
Interface
class BaseLog {
public error(...args: unknown[]): void;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
adze.error('An error occurred!');
// With emoji's enabled
adze.withEmoji.error('An error occurred!');
Browser Output

Server Output

warn
Use this for logging issues that may impact app performance in a less impactful way than an error.
Default log level = 2
Standard Log Method: console.warn()
Interface
class BaseLog {
public warn(...args: unknown[]): void;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
adze.warn("I'm warning you!");
// With emoji's enabled
adze.withEmoji.warn("I'm warning you!");
Browser Output

Server Output

info
Use this for logging general insights into your application. This level does not indicate any problems.
Default log level = 3
Standard Log Method: console.info()
Interface
class BaseLog {
public info(...args: unknown[]): void;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
adze.info('App information');
// With emoji's enabled
adze.withEmoji.info('App information');
Browser Output

Server Output

fail
Use this for logging network communication errors or other non-fatal errors that do not break your application.
Default log level = 4
Standard Log Method: console.info()
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class BaseLog {
public fail(...args: unknown[]): void;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
adze.fail('An operation failed to execute!');
// With emoji's enabled
adze.withEmoji.fail('An operation failed to execute!');
Browser Output

Server Output

success
Use this for logging successful network communications or other successful operations within your app.
Default log level = 5
Standard Log Method: console.info()
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class BaseLog {
public success(...args: unknown[]): void;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
adze.success('An operation was successful!');
// With emoji's enabled
adze.withEmoji.success('An operation was successful!');
Browser Output

Server Output

log
Use this for general logging that doesn't apply to any of the lower levels.
Default log level = 6
Standard Log Method: console.log()
Interface
class BaseLog {
public log(...args: unknown[]): void;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
adze.log('Logging a message.');
// With emoji's enabled
adze.withEmoji.log('Logging a message.');
Browser Output

Server Output

debug
Use this for logging information that you typically do not want to see unless you are debugging a problem with your application. This is typically hidden by default.
Default log level = 7
Standard Log Method: console.debug()
Interface
class BaseLog {
public debug(...args: unknown[]): void;
}
Example
import adze, { setup } from 'adze';
// We need to raise the active log level to see debug logs.
setup({
activeLevel: 'debug',
});
adze.debug('Debugging an issue.');
// With emoji's enabled
adze.withEmoji.debug('Debugging an issue.');
Browser Output

Server Output

verbose
Use this for logging extremely detailed debugging information. Use this level when the values you are logging are granular enough that they are no longer easily human readable.
Default log level = 8
Standard Log Method: console.debug()
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class BaseLog {
public verbose(...args: unknown[]): void;
}
Example
import adze, { setup } from 'adze';
// We need to raise the active log level to see verbose logs.
setup({
activeLevel: 'verbose',
});
adze.verbose('Logging some extreme detail.');
// With emoji's enabled
adze.withEmoji.verbose('Logging some extreme detail.');
Browser Output

Server Output

Other Terminators
Aside from the basic level terminator methods, Adze also exposes a few others for different utility purposes.
clear / clr
This terminator simply exists as an alias for console.clear().
Standard Log Method: console.clear()
Interface
class BaseLog {
public clear(): void;
public clr(): void;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
adze.log('This is a log to be cleared.');
adze.clear();
custom
Terminates the log at the provided custom log level. Custom log levels are defined within the Adze configuration object under the levels property. Adze can be configured by the setup function or by passing configuration to the seal or sealTag terminator.
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class BaseLog {
public custom(levelName: string, ...args: unknown[]): void;
}
Example
import adze, { setup } from 'adze';
setup({
levels: {
myLevel: {
levelName: 'myLevel',
level: 4,
method: 'info',
style:
'font-size: 12px; border-radius: 4px; padding-right: 10px; background: linear-gradient(to right, #ffcafc, #ff02f2); color: #fff; border-color: #e3bbbb;',
terminalStyle: ['white', 'bgMagenta'],
emoji: '👾',
},
},
});
adze.custom('myLevel', 'This is my custom log level.');
adze.withEmoji.custom('myLevel', 'This is my custom log level with an emoji.');
Browser Output

Server Output

seal
The seal terminator is used for creating child loggers.
It allows you to setup your child logger by writing a log chain as you normally would, except that instead of terminating it with a log level, you seal the configuration into a new log class.
The new log class inherits all of the configuration of your log chain.
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class BaseLog {
public seal(cfg?: UserConfiguration): SealedLog;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
const logger = adze.withEmoji.ns('my-app').seal();
logger.log('This is a log from my sealed child logger.');
Browser Output
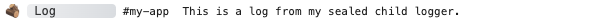
Server Output

sealTag
The sealTag terminator is used for creating child loggers for a specific log level that can be used as a convenient string template tag function.
For instance, if you find yourself logging errors in catch functions repeatedly, you can create an Err template tag function for logging the errors.
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class BaseLog {
public sealTag(method: string, cfg?: UserConfiguration): SealedLog;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
const ERR = adze.withEmoji.sealTag('error');
const url = 'http://www.example.com/';
try {
const res = fetch(url);
} catch (e) {
ERR`Failed to fetch from ${url}!`;
}
Browser Output

Server Output

thread
The thread terminator is used to create a Mapped Diagnostic Context where context values are recorded from multiple scopes but are output together in a single log. This is used in conjunction with the dump modifier for outputting the thread's values.
Refer to threading in the Getting Started guide for more information.
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class BaseLog {
public thread(key: string, value: unknown): void;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
function add(a: number, b: number) {
const answer = a + b;
adze.label('maths').thread('added', { a, b, answer });
return answer;
}
function subtract(x: number, y: number) {
const answer = x - y;
adze.label('maths').thread('subtracted', { x, y, answer });
return answer;
}
add(1, 2);
subtract(4, 3);
adze.label('maths').dump.info('Results from our thread');
Browser Output

Server Output
