Modifiers
Once you have an Adze log instance you can now start applying modifiers. Modifiers are methods that alter the log in some way and then return the log instance so that you may chain more modifiers or terminate the instance. Keep in mind, some modifiers have a dependency on the presence of a label and labels rely on GlobalStore.
assert
This modifier accepts an assertion boolean expression and will only print if the boolean expression fails (is a falsy value).
Interface
class Log {
public assert(expression: boolean): Log;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
const x = 2;
const y = 3;
// Let's assert that x and y should be equal
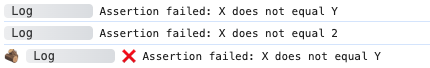
adze.assert(x === y).log('X does not equal Y');
// This log will not print because the assertion passes
adze.assert(x === 2).log('X does not equal 2');
// Let's look at the output with emoji's enabled
adze.withEmoji.assert(x === y).log('X does not equal Y');
Browser Output
Server Output

closeThread
This modifier closes a thread by deleting its tracked context from a shared label group.
This is used primarily in conjunction with a label and the thread terminator for implementing Threading.
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class Log {
public get closeThread(): Log;
}
Example
import adze, { setup } from 'adze';
function add(a: number, b: number) {
const answer = a + b;
adze.label('foo').thread('added', { a, b, answer });
return answer;
}
function subtract(x: number, y: number) {
const answer = x - y;
adze.label('foo').thread('subtracted', { x, y, answer });
return answer;
}
add(1, 2);
subtract(4, 3);
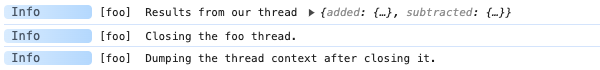
adze.label('foo').dump.info('Results from our thread');
adze.label('foo').closeThread.info('Closing the foo thread.');
adze.label('foo').dump.info('Dumping the thread context after closing it.');
Browser Output
Server Output

count
The count modifier tells the log to increment a counter associated to the log's label.
Interface
class Log {
public get count(): Log;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
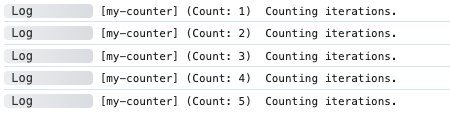
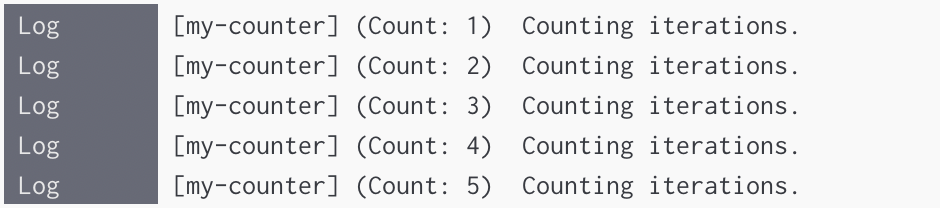
for (let i = 0; i < 5; i += 1) {
adze.label('my-counter').count.log('Counting iterations.');
}
Browser Output
Server Output
countClear
The countClear modifier completely clears the count from a label. Rather than setting the count to 0 it instead becomes null.
WARNING
This method is deliberately a modifier rather than a terminator because it forces you to write a log that gives you insight into when a counter was cleared. It also makes the countClear log recallable from the global store in the order it was created.
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class Log {
public get countClear(): Log;
}
Example
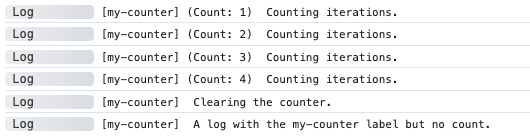
import adze from 'adze';
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i += 1) {
adze.label('my-counter').count.log('Counting iterations.');
}
adze.label('my-counter').countClear.log('Clearing the counter.');
adze.label('my-counter').log('A log with the my-counter label but no count.');
Output
countReset
The countReset modifier resets the counter associated to the log's label to 0.
WARNING
This method is deliberately a modifier rather than a terminator because it forces you to write a log that gives you insight into when a counter was reset. It also makes the countReset log recallable from the global store in the order it was created.
Interface
class Log {
public get countReset(): Log;
}
Example
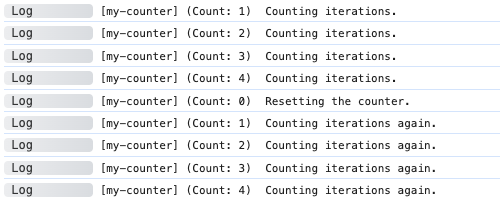
import adze from 'adze';
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i += 1) {
adze.label('my-counter').count.log('Counting iterations.');
}
adze.label('my-counter').countReset.log('Resetting the counter.');
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i += 1) {
adze.label('my-counter').count.log('Counting iterations again.');
}
Browser Output
Server Output
dir
The dir modifier transforms the output of the log by directing it to use the console.dir() method for printing purposes only.
WARNING
Logs that use dir as a modifier should only be given a single argument which is usually an object. If multiple arguments are given, behavior may differ between browser and server environments. Refer to the MDN docs for more details.
Interface
class Log {
public get dir(): Log;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
adze.dir.log({ foo: 'bar' });
Browser Output

Server Output

dirxml
The dirxml modifier transforms the output of the log by directing it to use the console.dirxml() method for printing purposes only. This is mainly useful for logging out DOM elements.
WARNING
Logs that use dirxml as a modifier should only be given a single argument which is usually a DOM Element or other XML object. If multiple arguments are given, behavior may differ between browser and server environments. Refer to the MDN docs for more details.
dirxml Interface
class Log {
public get dirxml(): Log;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
// create a new div element
const newDiv = document.createElement('div');
newDiv.setAttribute('id', 'test');
// and give it some content
const newContent = document.createTextNode('Hi there and greetings!');
// add the text node to the newly created div
newDiv.appendChild(newContent);
adze.dirxml.log(newDiv);
dump
This modifier instructs the labeled log to print the context values from a thread.
Refer to the threading section of the Getting Started guide for more information.
This modifier is dependent upon having a label.
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class Log {
public get dump(): Log;
}
Example
import adze, { setup } from 'adze';
const store = setup();
// Creating a GlobalStore listener is a great way to get meta data from your
// threaded logs to write to disk or pass to another plugin, library,
// or service.
store.addListener('*', (log) => {
// Do something with `log.data?.label?.context.added` or `log.data?.label?.context.subtracted`.
});
function add(a: number, b: number) {
const answer = a + b;
adze.label('foo').thread('added', { a, b, answer });
return answer;
}
function subtract(x: number, y: number) {
const answer = x - y;
adze.label('foo').thread('subtracted', { x, y, answer });
return answer;
}
add(1, 2);
subtract(4, 3);
adze.label('foo').dump.info('Results from our thread');
Browser Output

Server Output

format
The format modifier sets the formatter that will be used for the log. This can also be used in conjunction with the seal or sealTag terminators to create specifically formatted child loggers.
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class Log {
public format(format: string): Log;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
adze.format('standard').log('Logging a JSON formatted message.');
Browser Output

Server Output

group
The group modifier starts an uncollapsed group of logs. This means that all subsequent logs will be nested beneath this log until a groupEnd log occurs.
Interface
class Log {
public get group(): Log;
}
Example
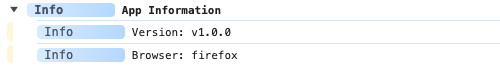
import adze from 'adze';
// Some info about our app.
const version = 'v1.0.0';
const browser = 'firefox';
adze.group.info('App Information');
adze.info(`Version: ${version}`);
adze.info(`Browser: ${browser}`);
adze.groupEnd.info();
Browser Output
Server Output

groupCollapsed
The groupCollapsed modifier starts an collapsed group of logs. This means that all subsequent logs will be nested beneath this log until a groupEnd log occurs.
WARNING
This will not be collapsed in a terminal environment since there is no way to uncollapse it.
Interface
class Log {
public get groupCollapsed(): Log;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
// Some info about our app.
const version = 'v1.0.0';
const browser = 'firefox';
adze.groupCollapsed.info('App Information');
adze.info(`Version: ${version}`);
adze.info(`Browser: ${browser}`);
adze.groupEnd.info();
Browser Output
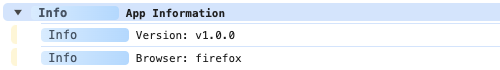
Server Output

groupEnd
The groupEnd modifier ends a log group. Any logs following a groupEnd will no longer be grouped.
Interface
class Log {
public get groupEnd(): Log;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
// Some info about our app.
const version = 'v1.0.0';
const browser = 'firefox';
adze.group.info('App Information');
adze.info(`Version: ${version}`);
adze.info(`Browser: ${browser}`);
adze.groupEnd.info(); // <-- Ends the group
adze.info('Some other information...');
Browser Output
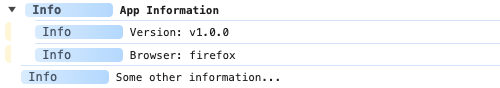
Server Output
if
This modifier accepts a boolean expression and will only print if the boolean expression passes (is a truthy value). This modifier is the opposite behavior of the assert modifier.
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class Log {
public if(expression: boolean): Log;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
const x = 2;
const y = 3;
// Print the log if x equals 2
adze.if(x === 2).log('X equals 2');
// This log will not print because the if fails
adze.if(x === y).log('X does not equal Y');
// Let's look at the output with emoji's enabled
adze.withEmoji.if(y === 3).log('Y equals 3');
Browser Output

Server Output

label
Applies an identifying label to a log. All logs that share the same label will be linked together in the Global Store. This enables global tracking for modifiers that require a label as a prerequisite.
These are the modifiers and terminators that require a label to be useful:
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class Log {
public label(name: string): Log;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
// Labels can be applied in any order in a modifier chain
adze.label('foo').count.log('Foo');
adze.count.label('foo').log('Bar');
Browser Output

Server Output

meta
The meta modifier allows you to attach meta data to your log instance. You can then retrieve it at a later time from within a log listener or by calling the data() method on a log instance.
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class Log {
// Types are Overloaded
public meta<T>(key: string, val: T): Log;
public meta<KV extends [string, any]>(...[key, val]: KV): Log;
}
Basic Example
import adze, { setup } from 'adze';
// Let's create a super important message to attach as meta data
const info = 'Hello World!';
adze.meta({ message: 'Hello world!' }).log('This log contains an important message.');
Example with Generic Type (TS Only)
import adze, { setup, type JsonLogFormatMeta } from 'adze';
// We'll setup our logger to output JSON.
setup({
format: 'json',
});
adze
// The type here ⬇️ ensures that you input the values required by the JSON formatter.
.meta<JsonLogFormatMeta>({ hostname: 'localhost', name: 'myapp' })
.log('This log contains an important message.');
Example with Listener
import adze, { setup } from 'adze';
// Let's optionally create a GlobalStore to show the use of meta data on listeners
const store = setup();
// We'll listen only to logs of level 6 which is "log"
store.addListener('log', (log) => {
adze.info("My log's meta data!", log.data?.meta);
});
adze.meta({ message: 'Hello world!' }).log('This log contains an important message.');
Browser Output from Listener

Server Output from Listener

namespace / ns
This modifier adds one or more namespaces to a log. These are mainly used as human readable group identifiers but are also useful for filtering logs and for identifying logs from a log listener. This modifier does not do any special grouping under the hood.
Multiple calls to the namespace modifier are additive by nature and will not overwrite previously applied namespaces. This is especially useful when working with sealed child loggers.
The ns() method is just a shorter alias for namespace().
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class Log {
public namespace(...ns: string[]): Log;
public ns(...ns: string[]): Log;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
adze.namespace('tix-123').log('Important info for a feature.');
adze
.namespace('tix-123', 'tix-456', 'tix-789')
.log('Multiple namespace entry simplified by the restof operator.');
// ns() is a shorthand alias for namespace()
adze.ns('tix-456').log('More info');
// Multiple calls to namespace/ns are additive
adze.ns('foo').ns('bar', 'baz').log('This log has all applied namespaces.');
Browser Output
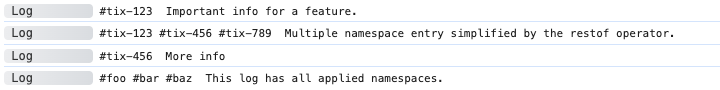
Server Output

Namespaces with Constraints
Adze also supports passing a constraints type when sealing a new logger or when calling the setup function. This is beneficial because it will force users to add any new namespace to the central constraints type. This will make it easier to filter namespaces throughout your application because you will only have a single place to reference to understand what namespaces are being used.
import adze, { setup } from 'adze';
// First we will create our app namespace constraints.
type AllowedNamespaces = 'foo' | 'bar' | 'hello' | 'world';
// We can apply it when we call the `setup` function, or...
setup<AllowedNamespaces>();
// Alternatively, we can apply the namespace constraint type when sealing a child logger.
const logger = adze.seal<AllowedNamespaces>();
// Now when we define namespaces for a log a type error will be thrown if the
// namespace provided isn't in the allowedNamespaces union type.
logger.ns('foo', 'bar', 'baz').fail('This is not allowed.');
// ~~~~~
// Argument of type '"baz"' is not assignable to parameter of type '"foo" | "bar" | "hello" | "world"'.
silent
The silent modifier allows a log to be terminated and cached but prevents it from printing to the console. Because the log is still processed, it will still trigger middleware hooks and listeners.
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class Log {
public get silent(): Log;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
adze.log('Knock knock!');
adze.silent.log('Crickets...');
adze.log('I guess nobody is home :(');
Browser Output

Server Output

table
The table modifier transforms the output of the log by directing it to use the console.table() method for printing purposes only.
Interface
class Log {
public get table(): Log;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
const tabular_data = [
{ firstName: 'Andrew', lastName: 'Stacy' },
{ firstName: 'Jim', lastName: 'Bob' },
];
adze.table.log(tabular_data);
Browser Output

Server Output

time
This modifier starts a timer associated to the log's label. This is useful for taking performance measurements. A log with a time modifier must be followed by a log with a timeEnd modifier in order to get the final measurement.
This modifier is dependent upon having a label.
Interface
class Log {
public get time(): Log;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
// Let's create a timer for performance
adze.label('loop').time.log('Starting a timer.');
for (let i = 0; i < 10000; i += 1) {
// Do a lot of stuff that takes time
}
// End the timer to get the loop performance
adze.label('loop').timeEnd.log('Performance of our loop.');
// Let's see the output with emoji's
adze.withEmoji.label('loop').timeEnd.log('Performance of our loop.');
Browser Output
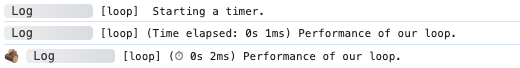
Server Output
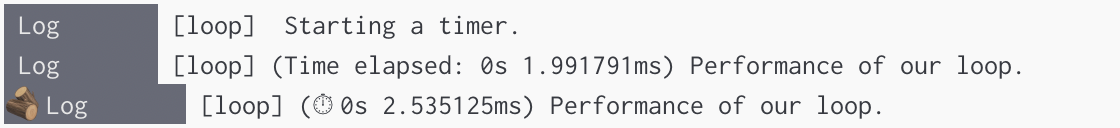
timeEnd
This modifier ends a timer associated to the log's label. This is useful for taking performance measurements. A log with a timeEnd modifier must be preceded by a log with a time modifier in order to get the final measurement.
This modifier is dependent upon having a label.
Interface
class Log {
public get time(): Log;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
// Let's create a timer for performance
adze.label('loop').time.log('Starting a timer.');
for (let i = 0; i < 10000; i += 1) {
// Do a lot of stuff that takes time
}
// End the timer to get the loop performance
adze.label('loop').timeEnd.log('Performance of our loop.');
// Let's see the output with emoji's
adze.withEmoji.label('loop').timeEnd.log('Performance of our loop.');
Browser Output

Server Output

timeNow
This modifier logs the time elapsed since the page has loaded. This is useful for measuring page load performance rather than performance of a particular piece of code.
This modifier is not dependent upon a label.
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class Log {
public get timeNow(): Log;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
for (let i = 0; i < 10000; i += 1) {
// Do a lot of stuff that takes time
}
// Let's create a timer for performance
adze.timeNow.log('Recording the time elapsed since page load.');
// Let's see what it looks like with emoji's enabled.
adze.withEmoji.timeNow.log('Recording the time elapsed since page load.');
Browser Output

Server Output

timestamp
This modifier instructs the log to render an ISO 8601 timestamp.
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class Log {
public get timestamp(): Log;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
adze.timestamp.log('This log has a timestamp.');
Browser Output

Server Output

trace
This modifier instructs the log to print a stacktrace using the standard console.trace() method.
WARNING
The styling for logs using this modifier varies by browser. Chrome will render the log message with proper styling while Firefox will only render the message unstyled.
Interface
class Log {
public get trace(): Log;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
adze.trace.log('Trying to find an issue...');
Browser Output
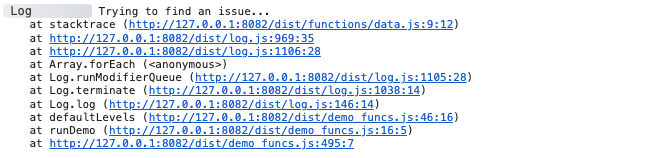
Server Output
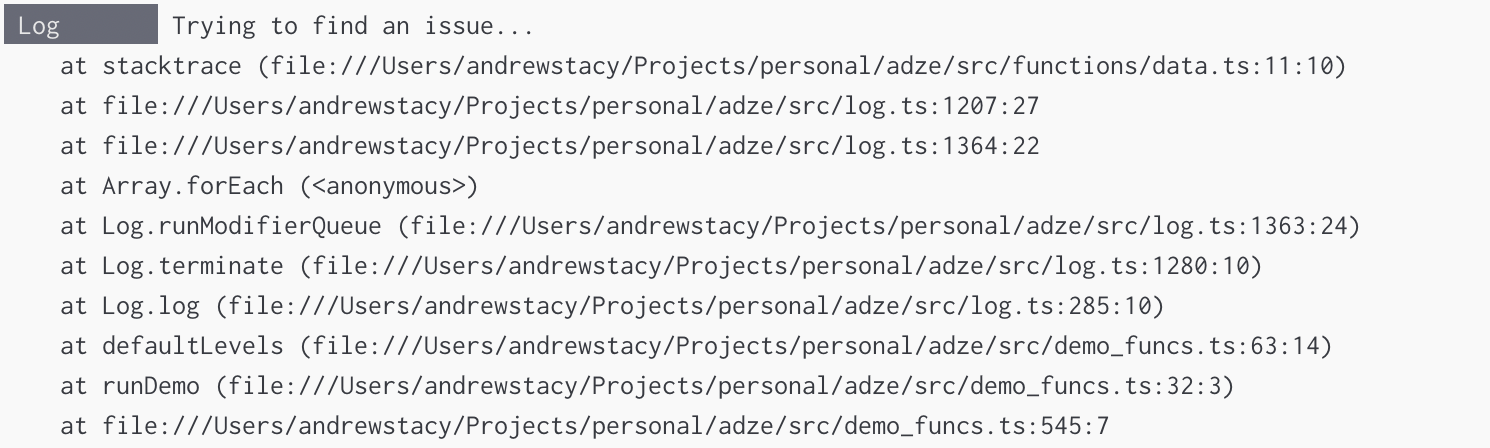
withEmoji
This modifier instructs the log to be printed with an emoji if the formatter supports it.
The only formatter that supports this out of the box is the pretty formatter.
This is not a standard API.
Interface
class Log {
public get withEmoji(): Log;
}
Example
import adze from 'adze';
adze.withEmoji.log('Logging with an emoji!');
Browser Output

Server Output
